What will you learn ?
What is A Method?
What is Polymorphism?
What do you mean by Method OverLoading?
In this blog let us look into a key concept in OOPS which is called Polymorphism.
What is a method?
A method in Java is a block of code that performs a specific task and can be called whenever required.
Now before diving into the details let us look into a real time analogy which makes the understanding much more better.
Say for instance there is a car company which will manufacture cars with new features every year now let us make a car company constant and try to play around with the new features it release every year and pass them as arguments into the car.
All these words may confuse you so let me make it much more simpler say the car company is Mercedes Benz and now first I would like to pass a feature called music system into the car this year.

In the second year I would like to improve the feature in the same car Mercedes Benz with a voice assist to make calls.
Now in the third year I would like to introduce a new feature in the same Mercedes Benz car which is AI which will take commands and say opens the sun roof.
Now here in the three years we are improving only features of the car not changing the car, so here polymorphism is nothing but a same object or method can behave differently in different parts of the code.
Method Overloading is a feature in Java that allows a class to have multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists.
Let us look at the code implementation for Method OverLoading:
public class Mercedes{
//Method 1
void addFeature(String music){
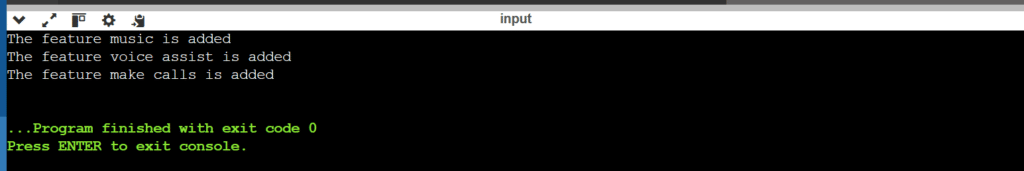
System.out.println("The feature music is added");
}
//Method 2
void addFeature(String music, String voice){
System.out.println("The feature voice assist is added");
}
//Method 3
void addFeature(String music, String voice, String makecall){
System.out.println("The feature make calls is added");
}
public static void main(String [] args){
Mercedes car = new Mercedes(); //new object initialization
car.addFeature("music"); //call for the method 1
car.addFeature("music","voice"); //call for method 2
car.addFeature("music","voice","makecall"); //call for method 3
}
}