Why do we use loops in C?
When we are given a task to print a line ten times then in a general case scenario, we keep writing the sentence ten times on a paper, but can it be done on the computer in the same way?
No because it will not be efficient, and not a good practice of coding here comes the use of loops.
Loop in general is a set of sequence of instruction which is repeated until a condition is reached.

Loops are classified into three types:
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Do-while Loop

For Loop:
It is used when a block of statement is to iterate for n number of times.
The syntax looks like:
for(initialisation;condition;updation){
//code;
}
Example: we have a task to print n natural numbers then which loop do we select?
It is for loop which is a tool for printing this numbers let us see how.
for(int i = 0; i<=n;i++){
printf(“The numbers are: %d\n“,i);
}
Let us see how do we add consecutive numbers?
The same code we repeat but the one change is we take a new variable a sum which will sum our i and the sum we get.
Code for printing n natural numbers:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int p = 0;
printf("Enter the number: ");
scanf("%d",&p);
for(int i = 0; i<=p; i++){
printf("%d\n", i);
}
}
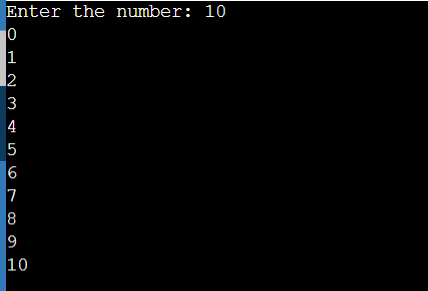
//Dry Run //0 --> 0 then it checks whether 1<10 it is less so 1 will be printed then it checks whether 2<10 it is less so 2 will be printed then it checks whether 3<10 it is less so 3 will be printed then it checks whether 4<10 it is less so 4 will be printed then it checks whether 5<10 it is less so 5 will be printed then it checks whether 6<10 it is less so 6 will be printed then it checks whether 7<10 it is less so 7 will be printed then it checks whether 8<10 it is less so 8 will be printed then it checks whether 9<10 it is less so 9 will be printed then it checks whether 10<=10 it is less so 10 will be printed
While Loop:
When we are to print a condition in the loop then we use the while loop which will prints it until the condition is achieved once it is done executing comes out of the loop.
//syntax
while(condition){
print something;
}
Example: we are given a condition where we must print a set of numbers then what to do?
First initialise a starting condition.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int p = 0;
while(p<11){
printf("%d\n", p);
p = p + 1;
}
}
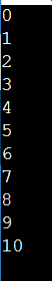
So, what is do-while loop?
When we are to do something first then run into the condition then how do we do that?
We use the do-while loop which will first execute a condition and then it runs into the loop condition.
The syntax looks like:
do
{
Print something;
}while(condition);
Code for printing numbers from 1 to 10:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int p = 0;
do{
printf("%d\n",p);
p = p + 1;
}while(p<11);
}